What is a 1099 MISC?
Confused by the 1099 MISC? Aren’t sure if you even need to fill it out? Payoneer workforce management has you covered with advice for freelancers and business owners alike.

IRS form 1099 MISC, also known as “Miscellaneous Information,” is a variant of form 1099, which is used to document income from sources other than a contractor’s payment (currently handled by 1099 NEC).
It is perhaps the most confusing variant of the 1099s, as the covered forms of income are numerous and, at times, feel random, as illustrated in the graphic below:
In addition to the seemingly random nature of the 1099 MISC, payers and payees have to take into account that these forms include income from bartering.
With these aspects in mind, the following article breaks down everything you need to know about the 1099 MISC, including information for the freelancer using it and the business owner filing and distributing it.
Who needs a 1099 MISC?
Form 1099 MISC is intended for contractors and other non-employees listing “reportable miscellaneous income” or “reportable payments” as they are referred to by the IRS.
The nature of these payments can make it difficult to know if you qualify.
If you are unsure whether or not you require a 1099 MISC, the following flowchart should help you determine if it is necessary:
We should note that, although referred to as ‘1099 misc independent contractors’, the 1099 MISC is not used to report independent contractor payments, as noted in question 2 of the flowchart. Rather, these payments fall under the 1099 NEC as of 2020.
What happens if the 1099 MISC is not filed correctly?
There are several deadlines surrounding your 1099 MISC that span the year:
1099 MISC milestones & deadlines
| Milestone | Deadline |
|---|---|
| Furnish Copy B to the recipient | January 31 |
| File Copy A (Paper) + Form 1096 with IRS | February 28 |
| File Copy A (Electronic) with IRS | March 31 |
| Correct 1099-MISC within 30 days (to avoid higher penalties) | February 28 (Non-leap year) |
| March 2nd (Leap year) | |
| Correct by August 1 (mid-tier penalty) | August 1 |
| Correct after August 1 (highest penalty) | On/After August 2 |
| File Form 945 for backup withholding (if applicable) | January 31 |
Improperly filed or missing 1099 MISCs can result in penalties determined by the IRS. These fees are determined on a case-by-case basis, but they vary between $60-$130 per instance, plus a $630 fine in the event of intentional disregard.
The following table provides a more detailed breakdown:
1099 MISC misfiling penalties
| Party | Failure Type | Average Penalty | |
| Payer | Late or Missing 1099-MISC to IRS | >30 days late | $60 per Form |
| By August 1 | $120 per Form | ||
| After August 1 | $310 Per Form | ||
| Intentional Disregard of Filing Rules | $630 per Form (no maximum cap) | ||
| Incorrect/TIN Mismatch on IRS Filing | $60 per return (same structure as late-filing) | ||
| Failure to Furnish to Recipient (Copy B) by January 31st | $60–$310 per form | ||
| Payee | Failure to Report Income on Tax Return | ≥20% of the underpayment due to unreported income | |
| Fraud or Intentional Understatement | 75% of the underpayment | ||
| Failure to File Their Own Tax Return Timely | 5% of the unpaid tax for each month the return is late, up to 25% of the unpaid tax | ||
The numbers listed above are per case, meaning that an employer who has issued 3 incorrect TINs would be liable for $180 rather than the $60 for a single case.
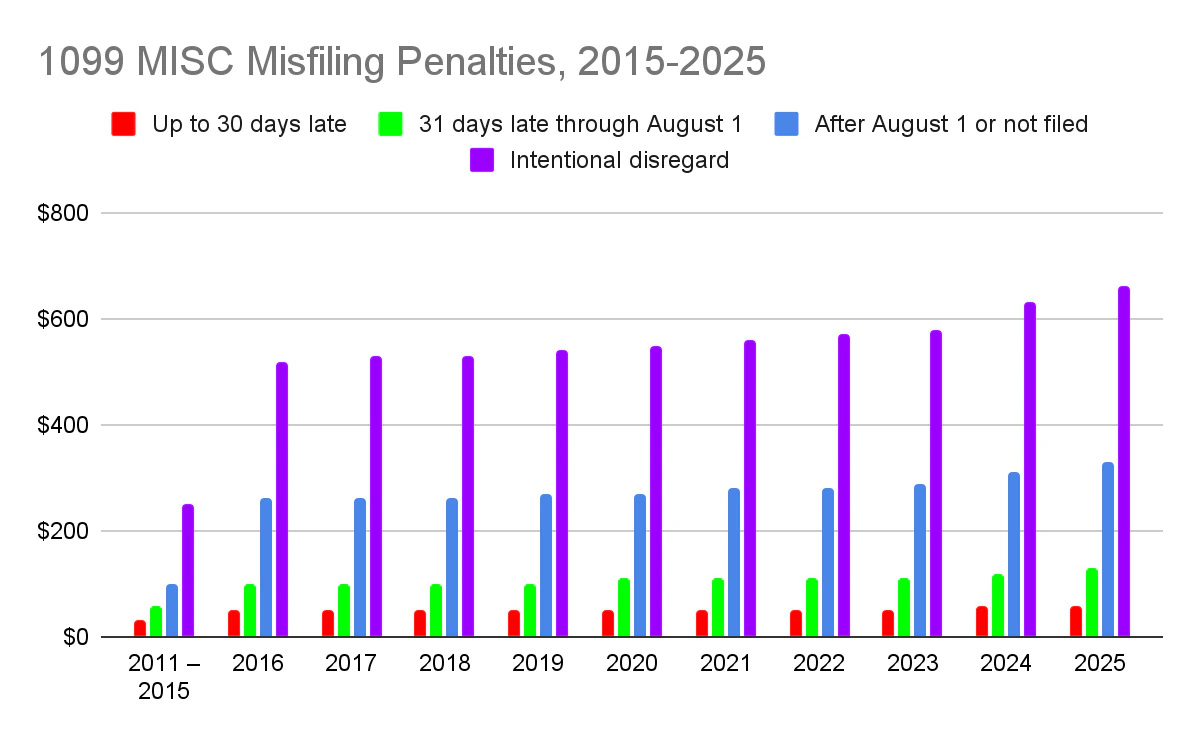
These filings have gotten more severe over the last 10 years, with the most significant increases experienced in the last two years. Freelancers and business owners working through a 1099 MISC should be aware of these trends and work under the assumption that they are likely to continue.
The following sections detail specific instructions for both independent contractors/freelancers as well as business owners, each of which have varied responsibilities around the 1099 MISC.
For freelancers
Freelancers have a relatively limited set of responsibilities around the 1099 MISC compared to the payer (i.e., the business owner issuing the payments). In short, they need to:
- Ensure they get their W9 correctly filled out and submitted to the payer before beginning any work
- Review the 1099 MISC when delivered by the payer
- Report the amounts on the 1099 MISC when filing your taxes
- Maintain 1099 MISC forms for the last five years in the event of an IRS audit
For business owners
The primary concern of business owners is to ensure that they issue and file a 1099 MISC with the payee and the IRS before the relevant deadlines. A summary of these deadlines is as follows:
How do I fill out a 1099 MISC?
The following table provides a box-by-box set of instructions to fill out a 1099 MISC, including plain language instructions for what needs to go in each box.
1099 MISC: Box-By-Box
| # | Item | What to Put Here |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Rents | Total rent over $600 received in the course of payer’s trade or business, if applicable |
| 2 | Royalties | Total royalties over $10 paid in the course of a trade or business, if applicable |
| 3 | Other income | Misc income that doesn’t go anywhere else on the form. Includes: Barter income Prizes awards Referral fees or finder’s fees |
| 4 | Fed. Income Tax Withheld | Amount of federal backup withholding withheld. Required at 24% if a proper TIN was not provided on the payee’s W9 |
| 5 | Fishing Boat Proceeds | Gross proceeds paid to the crew members of a fishing boat |
| 6 | Medical/Healthcare Payments | Amounts >$600 paid to medical providers for services rendered to the employees and patients |
| 7 | Direct Sales of $5,000 or More of Consumer Products for Resale | Check if the payer made a sale $5,000 or more of consumer products for resale (Ex. purchasing $5k of inventory with the intent to resell it) |
| 8 | Substitute Payments in Lieu of Dividends or Interest | Amounts paid instead of dividends or interest |
| 9 | Crop Insurance Proceeds | Report on Schedule F (Form 1040) |
| 10 | Gross Proceeds Paid to an Attorney | It’s what it sounds like. Only include the taxable amount |
| 11 | Fish Purchased for Resale | Amount (instructions specify cash) received for fish if you fish professionally |
| 12 | Section 409A Deferrals | Current year’s deferrals under an NQDC plan. May be blank, but is subject to section 409A requirements if filled |
| 13 | FACTA Filing Requirement | Check if you are: A U.S. payer filing 1099s as part of satisfying your requirement to report with respect to a U.S. account for chapter 4 of the Internal Revenue Code An FFI reporting payments to a U.S. account under an election described in Regulations section 1.1471-4(d)(5) (i)(A) |
| 14 | Blank | Reserved for future uses |
| 15 | Nonqualified Deferred Compensation | Includes: Income as a nonemployee under an NQDC plan that does not meet the requirements of section 409A. Any amount included in box 12 that is currently taxable |
| 16 | State Tax Withheld | N/A |
| 17 | State/Payer’s State No | N/A |
| 18 | State Income | N/A |
What do I do with my completed 1099 MISC?
Once your 1099 MISC has been filled out, several copies need to be sent to different destinations:
- Copy 1: Send to the recipient’s state tax department.
- Copy 2: Send to the recipient to file for their own state tax return.
- Copy B: Send this copy to the recipient for their records.
- Copy C: Retain this copy for your records.
What’s the best way to manage a 1099 MISC?
Business owners rarely calculate and file something as complex as a 1099 MISC manually; often, they work through a dedicated service that handles most or all of the process for them.
There are several options for this service, and which one specifically works for you depends on a few considerations. See the table below for more:
1099 MISC management options
| Method | Strengths | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Global Payroll/Payments Service Provider | Tax document management, in addition to workforce management tools | Companies seeking rapid scaling for ongoing contractor relationships |
| Tax Filing Software | ERP integrations and automated processes, but the interface can be confusing | Enterprise-level companies bringing multiple processes under one roof |
| Doc Management | Easy implementation and automated fill prompts, but often has per-transaction fees | Companies with in-house HR |
| Manual Filing | Ensures the most accurate form is used, but requires the most work | Very small operations and one-time jobs |
Payoneer Workforce Management for managing contractors
Working with a comprehensive workforce management provider is typically the preferred method for getting support and guidance to manage tax documentation due to the extent of coverage and the relative level of expertise they provide compared to other options.
Providers like Payoneer Workforce Management facilitate global contractor management, allowing you to scale your workforce with international talent by streamlining the complexities of local compliance laws.
Reach out to us at the link below if you are ready to learn more.
FAQs
1) What does a 1099-MISC do?
The 1099-MISC is a tax form that reports miscellaneous income, including non-employee payments of $600 or more and royalty payments of $10 or more, received during a calendar year.
2) Do I have to enter my 1099-MISC?
If you have a 1099-MISC, enter it on the “Your 1099-NEC or 1099-MISC Income” screen, where you can specify whether the income is related to a business (Schedule C), rental or royalty (Schedule E), farm (Schedule F), farm rental (Form 4835), or should be reported as Other Income (Schedule 1).
Related resources
Latest articles
-
Looking for an employer of record in Moldova? Here’s what you need to know
Explore how Payoneer Workforce Management helps manage onboarding, payroll, benefits and more in the Republic of Moldova, while simplifying talent engagement in the country.
-
PayPal to Payoneer: All You Need to Know
Learn how to transfer money from PayPal to Payoneer, compare fees, and explore alternatives for users in Pakistan. A complete guide to linking Payoneer and PayPal.
-
How to Use Data Analytics to Improve Payment Processing Efficiency
Learn how to leverage payment data analytics to optimise payment processing efficiency, reduce transaction costs, improve approvals, and gain actionable insights.
-
Payment Confirmation Guide: How to Know Your Money Arrived Safely
Learn how to confirm your payment was received, track its status, and understand typical processing times with Payoneer’s international payment tools.
-
Using an Employer of Record in Taiwan
Learn how an Employer of Record in Taiwan helps you onboard, pay, and manage talent without a local entity. This blog also covers essential information on Taiwanese payroll, labor laws, leave policies, and more.
-
Using an employer of record in Sri Lanka
Explore key Sri Lankan legal regulations and employment nuances that you need to keep track of. Learn how you can utilize an EOR in Sri Lanka to support local team expansion, including onboarding, payroll, benefits, and more.
Disclaimer
The information in this article/on this page is intended for marketing and informational purposes only and does not constitute legal, financial, tax, or professional advice in any context. Payoneer and Payoneer Workforce Management are not liable for the accuracy, completeness or reliability of the information provided herein. Any opinions expressed are those of the individual author and may not reflect the views of Payoneer or Payoneer Workforce Management. All representations and warranties regarding the information presented are disclaimed. The information in this article/on this page reflects the details available at the time of publication. For the most up-to-date information, please consult a Payoneer and/or Payoneer Workforce Management representative or account executive.
Availability of cards and other products is subject to customer’s eligibility. Not all products are available in all jurisdictions in the same manner. Nothing herein should be understood as solicitation outside the jurisdiction where Payoneer Inc. or its affiliates is licensed to engage in payment services, unless permitted by applicable laws. Depending on or your eligibility, you may be offered the Corporate Purchasing Mastercard, issued by First Century Bank, N.A., under a license by Mastercard® and provided to you by Payoneer Inc., or the Payoneer Business Premium Debit Mastercard®, issued and provided from Ireland by Payoneer Europe Limited under a license by Mastercard®.
Skuad Pte Limited (a Payoneer group company) and its affiliates & subsidiaries provide EoR, AoR, and contractor management services.














