IRS 20-point checklist for independent contractors
Need a quick and easy way to navigate your IRS 20-point checklist? Look no further. Payoneer Workforce Management team provides a free online checklist with PDF download.

The IRS 20-point checklist (also referred to as the “employee vs contractor checklist” sometimes) is a set of guidelines created in 1987 under IRS Revenue Ruling 87-41 to determine whether a new worker would be classified as an employee or a contractor. Due to the heavy fines and penalties associated with misclassification, it has become an essential tool for onboarding and HR.
Unfortunately, utilizing the traditional checklist can be confusing. Employees inevitably fall into gray areas between classifications, and the phrasing of certain questions leaves significant room for interpretation.
So, we have created the following resource for business owners to easily run through the IRS 20-point checklist, as presented below.
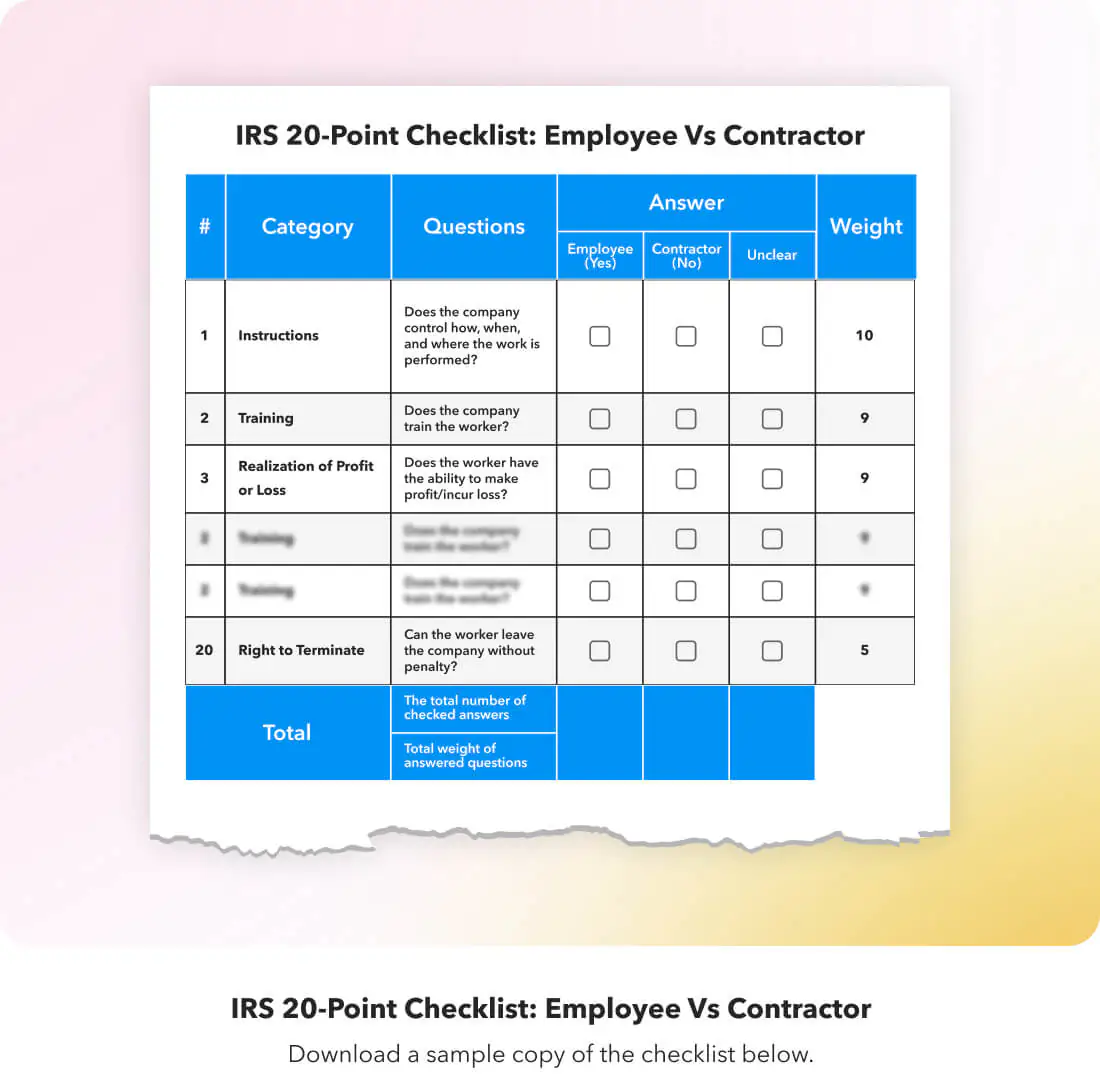
How do I use the IRS 20-point checklist?
Although none of the 20 points are explicitly more important than the others, the IRS (as well as the courts) has historically leaned on certain points more than others, prioritizing a “totality-of-the-circumstances” analysis.
To provide a sense of these leanings, we have included a subjective 1-10 score for each point, indicating how much they “weigh.”
With that in mind, here’s a quick breakdown of how to use our IRS 20-point checklist:
- Answer each question as best you can. Include notes where necessary.
- Calculate totals for number and weight. The number is important, but weight is most important. If the results are unclear, revisit the position being offered to ensure that terms are clearly stated, and speak with a specialist if you are still having difficulty.
- Take a gut check. Remember, the checklist is not perfect; a result indicating one way may actually be another when considering the totality of the circumstances. If you are unsure at this stage, speak with a specialist, as discussed in the sections below.
- Take action
- If employee: Begin work with HR filing a W2
- If contractor: Review contractor agreement
A simpler way to qualitatively evaluate this question is to consider how much power the worker has in their relationship with the company; do they operate like a business, with other clients they provide services to, or do they operate under the company’s control?
IRS 20-Point Checklist: Employee vs Contractor
Are there any “rules of thumb” I should know?
When running a new worker through the IRS 20-point checklist, there are a few things you should keep in mind:
- Be sure to document your reasoning: Misclassification is the central concern surrounding the employee vs contractor checklist, so write down why you answered a question a certain way, especially in cases where the answer falls into a gray area. In the event your company is ever audited, these records can make the difference between paying back taxes, penalties, and liabilities.
- Be cautious: Err on the side of “Employee” when you are genuinely not sure how to answer a question, as the penalties for misclassifying a contractor as an employee are significantly less severe than those for misclassifying an employee as a contractor.
- Consult an expert if you are unsure: If you have completed the employee vs contractor checklist and are still unsure of how to proceed, it’s best to work with a specialist in this area. Consult employment attorneys, tax attorneys, CPAs, or HR compliance consultants.
If you want to make the process easier on yourself, however, global payroll or EOR providers offer business owners the means to reduce misclassification errors before they ever occur.
Still unsure of how to implement your employee vs contractor checklist?
It’s perfectly normal to feel overwhelmed when onboarding new talent. Using the IRS 20-point checklist is meant to be more of a qualitative practice than a quantitative science, which is often the source of confusion and stress.
If you would like to have a PDF, you are free to download it here.
If you would like to get an expert opinion on your onboarding practices, our best advice is to work with an expert.
Payoneer Workforce Management provides a suite of services to hire, onboard, and manage employees in your business ecosystem.
Related resources
Latest articles
-
Looking for an employer of record in Moldova? Here’s what you need to know
Explore how Payoneer Workforce Management helps manage onboarding, payroll, benefits and more in the Republic of Moldova, while simplifying talent engagement in the country.
-
PayPal to Payoneer: All You Need to Know
Learn how to transfer money from PayPal to Payoneer, compare fees, and explore alternatives for users in Pakistan. A complete guide to linking Payoneer and PayPal.
-
How to Use Data Analytics to Improve Payment Processing Efficiency
Learn how to leverage payment data analytics to optimise payment processing efficiency, reduce transaction costs, improve approvals, and gain actionable insights.
-
Payment Confirmation Guide: How to Know Your Money Arrived Safely
Learn how to confirm your payment was received, track its status, and understand typical processing times with Payoneer’s international payment tools.
-
Using an Employer of Record in Taiwan
Learn how an Employer of Record in Taiwan helps you onboard, pay, and manage talent without a local entity. This blog also covers essential information on Taiwanese payroll, labor laws, leave policies, and more.
-
Using an employer of record in Sri Lanka
Explore key Sri Lankan legal regulations and employment nuances that you need to keep track of. Learn how you can utilize an EOR in Sri Lanka to support local team expansion, including onboarding, payroll, benefits, and more.
Disclaimer
The information in this article/on this page is intended for marketing and informational purposes only and does not constitute legal, financial, tax, or professional advice in any context. Payoneer and Payoneer Workforce Management are not liable for the accuracy, completeness or reliability of the information provided herein. Any opinions expressed are those of the individual author and may not reflect the views of Payoneer or Payoneer Workforce Management. All representations and warranties regarding the information presented are disclaimed. The information in this article/on this page reflects the details available at the time of publication. For the most up-to-date information, please consult a Payoneer and/or Payoneer Workforce Management representative or account executive.
Availability of cards and other products is subject to customer’s eligibility. Not all products are available in all jurisdictions in the same manner. Nothing herein should be understood as solicitation outside the jurisdiction where Payoneer Inc. or its affiliates is licensed to engage in payment services, unless permitted by applicable laws. Depending on or your eligibility, you may be offered the Corporate Purchasing Mastercard, issued by First Century Bank, N.A., under a license by Mastercard® and provided to you by Payoneer Inc., or the Payoneer Business Premium Debit Mastercard®, issued and provided from Ireland by Payoneer Europe Limited under a license by Mastercard®.
Skuad Pte Limited (a Payoneer group company) and its affiliates & subsidiaries provide EoR, AoR, and contractor management services.














