Pros and Cons of being a 1099 employee
Considering the pros and cons of being a 1099 employee/worker? We’ve got you covered here, breaking this classification down by area and showing how it compares to a W-2.

| A Note on Terminology: A “1099 employee” is not the correct terminology, but we use it several times here to ensure that those who need to find it do. “1099” refers to independent contractor status, while an “employee” operates through a W-2 rather than a 1099. These represent two different classifications of workers, the third being volunteers. |
The following table details the pros and cons of being a 1099 worker. For easy analysis, we split our evaluation into major categories concerning contractors (e.g., job security, freedom, taxes) and include summaries of pros and cons.
The Pros and Cons of Being a 1099 worker
| Pros | Cons | |
|---|---|---|
| Job Security | Typically protected by contract | No guarantee of contract renewals |
| Taxes | More opportunities for exemptions, etc | Have to calculate, track, and file yourself |
| Payment | The contractor sets their own rates | Heavier taxation rate |
| Workplace | The contractor determines the workplace | Often siloed from employees |
| Freedom | The contractor determines how work is done | You are responsible for the work |
The sections below provide a more in-depth look at the categories discussed in the table above to provide more clarity. In addition, we provide suggestions for workers considering the pros and cons of being a 1099 worker to get started.
1. Job Security
1099 contractors typically operate on a by-project basis, which offers a true double-edged sword in terms of job security.
- On one hand, contractors have greater job security for the duration of the contract. Many employees provide work under an “at-will” employment status; this means that an employer can terminate an employee at any time for any reason. By contrast, contractors are protected by the terms of the contract, which typically has a carefully worded termination clause.
- On the other hand, contractors have virtually no job security at all once the contract is completed. It is entirely up to the employer whether they want to continue working with them at that point, meaning that contractors can often find themselves completely without work very quickly.
This means that contractors face a greater level of pressure to foster client relationships and ensure that clients are satisfied with the work being delivered to better forecast their future labor needs.
2. Taxes
Independent contractors are responsible for calculating and paying their taxes. On its face, this is both a greater responsibility and a higher level of taxes being paid:
1099 Contractor vs W-2 Employee: Taxes
| Tax Type | W-2 Employee | 1099 Contractor |
|---|---|---|
| State Income Tax | Withheld (if applicable) | Paid directly (if applicable) |
| Federal Income Tax | Withheld from paycheck | Paid directly |
| Tax Withholding | Automatic | Quarterly payments |
Additionally, Social Security, Medicare, and FICA/Self-Employment Tax are also applicable; please check the official IRS site for current rates.
That being said, independent contractors also have the opportunity to claim extensive deductions and exemptions on their taxes, which are not available to W-2 employees. A non-comprehensive list of these exemptions includes:
1099 Contractor Tax Deductions
| Deduction Type | Total Amount Saved | How to Qualify |
|---|---|---|
| Self-Employment Tax Deduction | Reduces taxable income by half of your SE tax | Pay self-employment tax; claim on Schedule 1 and Schedule SE |
| Home Office Deduction | Up to $1,500 (simplified) or % of actual costs | Use part of home regularly & exclusively for business; claim on Form 8829/Schedule C |
| Phone & Internet | Business-use portion only | Must be used for business; deduct only business portion; keep records |
| Business Supplies/Equipment | 100% if used for business | Must be ordinary/necessary for business; keep receipts |
| Business Travel & Meals | All business travel, 50% of meals | Travel must be for business; keep detailed records/receipts |
| Health Insurance Premiums | 100% of premiums paid | Must not be eligible for employer plan; self-employed; claim on Form 1040 |
It is the contractor’s responsibility to manage filing these things on their own, which is often the sticking point for workers considering 1099 status but not wanting to do that much labor to profit.
3. Payment
1099 contractors are typically paid on a per-contract basis, sometimes metered out as they hit agreed-upon milestones. For example, a writer might be paid upon delivery of a rough draft, another percentage when they complete initial edits, and the final portion when the article is published.
The exact rate is determined by the contractor themselves, but is often based on existing benchmarks based on relative experience and the industry in which they work. The graph below provides a few rough averages:
Average contractor pay by industry & skill level
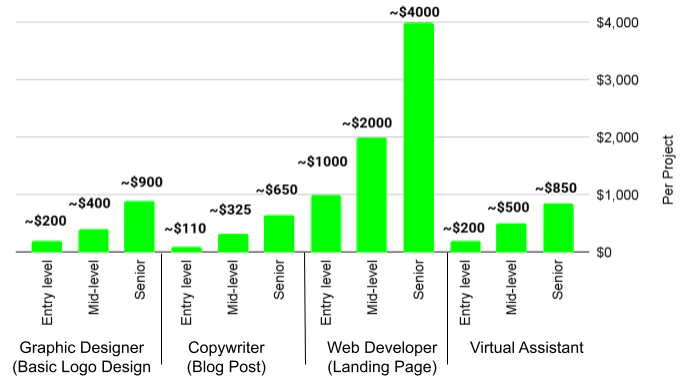
These figures are assumed in a general sense; actual numbers may vary based on the contractor, location, and role.
Similar to their relationship with taxes, benefitting from the higher wages that a 1099 contractor can earn requires a great deal of effort to assess your own abilities even while you negotiate with new prospective employers. Workers who see this as an opportunity rather than a liability may be well-suited for a career as freelancers.
4. Workplace
Contractors and freelancers determine the conditions under which they work. In order to save costs, many choose to work from home where possible, often resulting in a more casual work environment. This can mean, however, that they are less connected to the rest of an employer’s employees, which can lead to potential issues with communication and transparency that the contractor will need to negotiate.
5. Freedom
One of the biggest draws for prospective contractors is the ability to determine their own schedule and negotiate the terms under which they work.
Contractors perform their job according to their own ability, having to abide only by the stipulations of the contract as an external guide, but otherwise, they are completely free to work however they please.
While this is seen as a boon by most people, the reality is that operating as a 1099 contractor means operating without a safety net; at the end of the day, you are responsible for the work you contract out.
Fail to perform up to par with the client’s expectations (e.g., turning in late or unsatisfactory work, being unavailable for contact, having unpleasant interactions with a client), and they will likely cut you loose.
Is it Better to be a W-2 Employee?
If you are reading through the pros and cons of a 1099 and paying more attention to the cons, employee status might seem more appropriate. Many workers select this lifestyle because of the ease it provides, but it also comes with disadvantages:
1099 Contractor vs W-2 Employee: Pros and Cons
| 1099 Contractor | W-2 Employee | |
|---|---|---|
| Pros | Control over when and how work is done | Higher job security |
| More opportunities for tax exemptions, etc | Employer handles taxes & benefits | |
| Cons | Lower job security | No control over job conditions |
| Have to file taxes yourself | Income is determined by the employer | |
| Best For Workers who Value… | Freedom, control, profit | Security, consistency, simplicity |
Still unsure?
The reality is that for all of the pros and cons of being a 1099 employee, there isn’t really a “right” decision. There’s only what’s right for you.
Often, we find that one of the biggest things holding workers back from embracing a 1099 lifestyle is the lack of tools to help manage what effectively becomes your own business.
These services can be hard to find, but they do exist; Payoneer Workforce management, for example, offers services to support freelancers/contractors, allowing them to create and send invoices; while supporting businesses to pay contractors in 70 currencies.
Book a demo today to learn about how we can offer support with contractor management.
Related resources
Latest articles
-
Looking for an employer of record in Moldova? Here’s what you need to know
Explore how Payoneer Workforce Management helps manage onboarding, payroll, benefits and more in the Republic of Moldova, while simplifying talent engagement in the country.
-
PayPal to Payoneer: All You Need to Know
Learn how to transfer money from PayPal to Payoneer, compare fees, and explore alternatives for users in Pakistan. A complete guide to linking Payoneer and PayPal.
-
How to Use Data Analytics to Improve Payment Processing Efficiency
Learn how to leverage payment data analytics to optimise payment processing efficiency, reduce transaction costs, improve approvals, and gain actionable insights.
-
Payment Confirmation Guide: How to Know Your Money Arrived Safely
Learn how to confirm your payment was received, track its status, and understand typical processing times with Payoneer’s international payment tools.
-
Using an Employer of Record in Taiwan
Learn how an Employer of Record in Taiwan helps you onboard, pay, and manage talent without a local entity. This blog also covers essential information on Taiwanese payroll, labor laws, leave policies, and more.
-
Using an employer of record in Sri Lanka
Explore key Sri Lankan legal regulations and employment nuances that you need to keep track of. Learn how you can utilize an EOR in Sri Lanka to support local team expansion, including onboarding, payroll, benefits, and more.
Disclaimer
The information in this article/on this page is intended for marketing and informational purposes only and does not constitute legal, financial, tax, or professional advice in any context. Payoneer and Payoneer Workforce Management are not liable for the accuracy, completeness or reliability of the information provided herein. Any opinions expressed are those of the individual author and may not reflect the views of Payoneer or Payoneer Workforce Management. All representations and warranties regarding the information presented are disclaimed. The information in this article/on this page reflects the details available at the time of publication. For the most up-to-date information, please consult a Payoneer and/or Payoneer Workforce Management representative or account executive.
Availability of cards and other products is subject to customer’s eligibility. Not all products are available in all jurisdictions in the same manner. Nothing herein should be understood as solicitation outside the jurisdiction where Payoneer Inc. or its affiliates is licensed to engage in payment services, unless permitted by applicable laws. Depending on or your eligibility, you may be offered the Corporate Purchasing Mastercard, issued by First Century Bank, N.A., under a license by Mastercard® and provided to you by Payoneer Inc., or the Payoneer Business Premium Debit Mastercard®, issued and provided from Ireland by Payoneer Europe Limited under a license by Mastercard®.
Skuad Pte Limited (a Payoneer group company) and its affiliates & subsidiaries provide EoR, AoR, and contractor management services.














